Change of State
Change of State: Overview
In this topic, we will learn the processes involved in changing the state of matter from one form to another. It also explains the melting point, boiling point, latent heat and its type with the help of graphs and illustrations.
Important Questions on Change of State
An ice cube is heated and the variation of its temperature with time is shown. The process representing the conversion of water into steam is
The physical quantity that determines whether or not a given system is in thermal equilibrium with another system is called
The unit of latent heat is_____?
Is latent heat released during sublimation?
What is the latent heat of condensation?
Is latent heat released during sublimation?
What is the melting point the same as?
What is the melting point and boiling point of the substance?
How do you find the boiling point of a substance?
A thermos bottle containing coffee is vigorously shaken. If the coffee is considered a system, then the temperature of the coffee will
Match the following?
|
|
Column |
|
Column |
|
Conversion of solid into liquid is |
Regelation |
||
|
Conversion of liquid into vapour is |
Sublimation |
||
|
Conversion of solid into vapour directly is |
Fusion |
||
|
Melting of ice caused by pressure is |
Vaporization |
The amount of heat required to convert a unit mass of solid into gas is
Observe the following temperature Vs. time graph and fill in the blank:
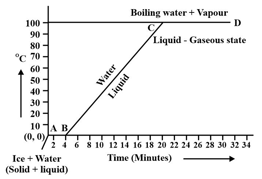
During transition of solid phase to liquid, the object absorbs _____ energy, but its temperature does not increase.
A block of ice at is slowly heated and converted to steam at . Which of the following curves represent the phenomenon qualitatively?
Two systems are in thermal equilibrium. The quantity which is common for them is
Select the examples of regelation from the following.
The phenomenon in which the ice converts to liquid due to applied pressure and then re-converts to ice once the pressure is removed is called _____.
Latent heat depends on the mass of the substance.
The ice melts at a temperature lower than on application of pressure.
